 Am I the only one that is getting confused by the increasing number of initiatives that the government is rolling out to encourage entrepreneurship? Or frustrated because they don’t actually seem to make a difference?
Am I the only one that is getting confused by the increasing number of initiatives that the government is rolling out to encourage entrepreneurship? Or frustrated because they don’t actually seem to make a difference?
We had Business Link, then we didn’t, except it still exists as a “business advice and guidance service portal”.
The Small Firms Loan Guarantee scheme (SFLG) has been around for decades and continues to help companies that need a bank loan. Or it would if the banks fulfilled their part of the deal by releasing the funds.
To encourage them to do so the government set up Project Merlin last year whereby the banks agreed to lend £76B specifically to small firms. However it has been a failure and banks are still holding on to their money. Now Merlin looks like being dumped along with any credibility that the banks could have gained by making good on their promises.
For some time now we’ve had the Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS) to encourage Investors, by giving them various tax breaks if they help to fund growing businesses.
In addition last year the Chancellor announced the Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS) due to come into effect on the 6th April 2012. This is aimed at small start-ups and gives a 50% tax relief to Investors. I’ll do a write up of that shortly, but it looks promising in motivating Investors.
Enterprise Zones were introduced to mixed response and the jury is out on their long-term effectiveness.
The Government has pushed StartupBritain which they call “a national campaign by entrepreneurs for entrepreneurs, harnessing the expertise and passion of Britain’s leading businesspeople to celebrate, inspire and accelerate enterprise in the UK”. Fine words – but never-the-less just words.
Talking about fine words, recently the latest campaign is “There’s a business in you”, which provides inspiring stories and highlights support available. However most of the highlighted support simply takes you to the Business Link website.
Then there’s talk about cutting Red Tape. There is a “Red Tape Challenge”, where members of the public can suggest red tape to be cut and a “1 in, 1 out” idea that says if a department wants to bring in a piece of legislation, they must first remove one. Latest government news is that there have been 19 in and 33 out, saving small businesses £3.2 B a year. What shall we spend it on?
How about making tax simpler and easier to understand I hear you say. Well there’s a government office called “The office for Tax Simplification”. Yes there really is, let’s hope they are successful.
So is it all spin and gimmicks as some business experts have commented, or a well co-ordinated and ambitious campaign to release the entrepreneurial spirit in us all and make Britain great again?

 I had a call from a director of a business that I occasionally provide with mentoring to ask me to come round asap. Over the Xmas break he had been having second thoughts about carrying the activity on, even though it was profitable.
I had a call from a director of a business that I occasionally provide with mentoring to ask me to come round asap. Over the Xmas break he had been having second thoughts about carrying the activity on, even though it was profitable. After writing the title of this piece I thought what more can I say? That’s it isn’t it? Provide a better service than your competitors and you will win business.
After writing the title of this piece I thought what more can I say? That’s it isn’t it? Provide a better service than your competitors and you will win business. “How do I get an Investor?” is the question I most get asked by entrepreneurs. Finding an Investor is often a hard and very time-consuming part of growing a business, but thousands of companies manage to do it every year.
“How do I get an Investor?” is the question I most get asked by entrepreneurs. Finding an Investor is often a hard and very time-consuming part of growing a business, but thousands of companies manage to do it every year. I must admit this blog sounds a bit as though I’m standing on a soap-box, but a recent comment by Google’s chairman, Eric Schmidt, rang true with me. He said:
I must admit this blog sounds a bit as though I’m standing on a soap-box, but a recent comment by Google’s chairman, Eric Schmidt, rang true with me. He said: Enterprise Zones are the latest government incentive to get businesses growing. Within the Enterprise Zone you can get superfast broadband, lower rates & taxes, and low levels of regulation & planning controls.
Enterprise Zones are the latest government incentive to get businesses growing. Within the Enterprise Zone you can get superfast broadband, lower rates & taxes, and low levels of regulation & planning controls. Almost all businesses now days have to have a web site. Even if you don’t sell over the web, your customers will expect to be able to find you on it.
Almost all businesses now days have to have a web site. Even if you don’t sell over the web, your customers will expect to be able to find you on it. Whenever I hear advice from successful entrepreneurs the most consistent mantra is “always hire the best people you can afford”.
Whenever I hear advice from successful entrepreneurs the most consistent mantra is “always hire the best people you can afford”.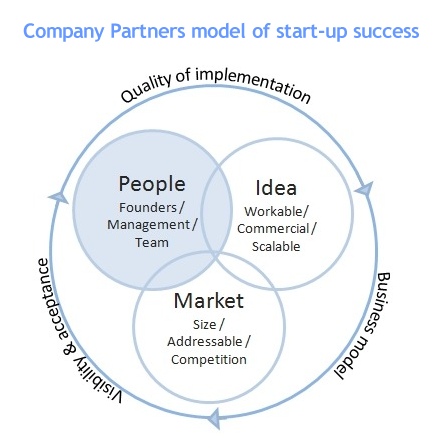
 I spent an enjoyable couple of days doing one-to-ones on business planning at a conference last week and the area that was most misunderstood was the need to define and understand your market.
I spent an enjoyable couple of days doing one-to-ones on business planning at a conference last week and the area that was most misunderstood was the need to define and understand your market.